집에서 쇼룸을 실행해보려고 했더니 다음과같은 오류가 발생했다.
Error: error:0308010C:digital envelope routines::unsupported
at new Hash (node:internal/crypto/hash:67:19)
at Object.createHash (node:crypto:130:10)
at module.exports (/Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/webpack/lib/util/createHash.js:135:53)
at NormalModule._initBuildHash (/Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/webpack/lib/NormalModule.js:417:16)
at handleParseError (/Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/webpack/lib/NormalModule.js:471:10)
at /Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/webpack/lib/NormalModule.js:503:5
at /Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/webpack/lib/NormalModule.js:358:12
at /Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/loader-runner/lib/LoaderRunner.js:373:3
at iterateNormalLoaders (/Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/loader-runner/lib/LoaderRunner.js:214:10)
at iterateNormalLoaders (/Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/loader-runner/lib/LoaderRunner.js:221:10)
/Users/user/Programming Documents/WebServer/untitled/node_modules/react-scripts/scripts/start.js:19
throw err;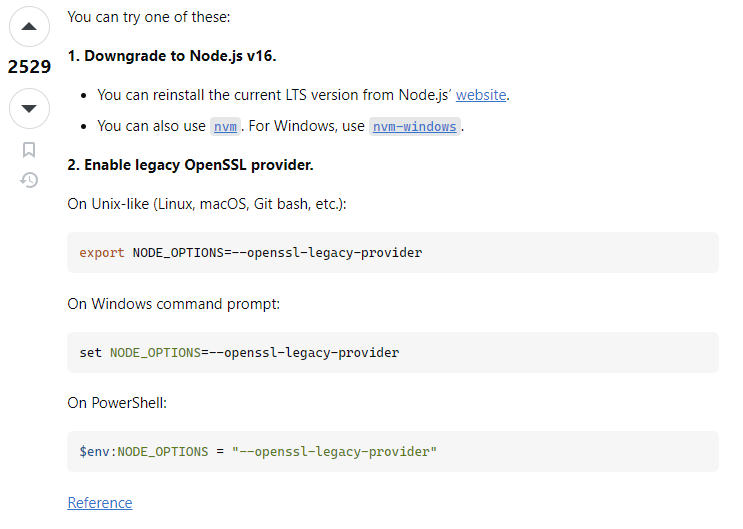
검색해보니 Node.js 내부에서 openssl (암호화) 관련 소스에서 발생하는 에러 같았다.
환경설정 옵션을 변경해주면 해결이 되는 듯 하다.